Diamond Education
Our diamond education is the most comprehensive diamond buying guide designed to answer all your questions. We address the 4 C’s of diamonds (carat, cut, color and clarity) and beyond so you can make the best decision when buying a diamond. Diamonds are considered the world’s most precious gemstones. They are traditionally used for engagement rings and other jewelry as a symbol of love and commitment. Buying a diamond is an important personal, financial, and emotional decision. Our gemologists are experts on the subject and provide invaluable guidance so you can shop with confidence in a pressure free environment.
The 4 Cs Of Diamonds
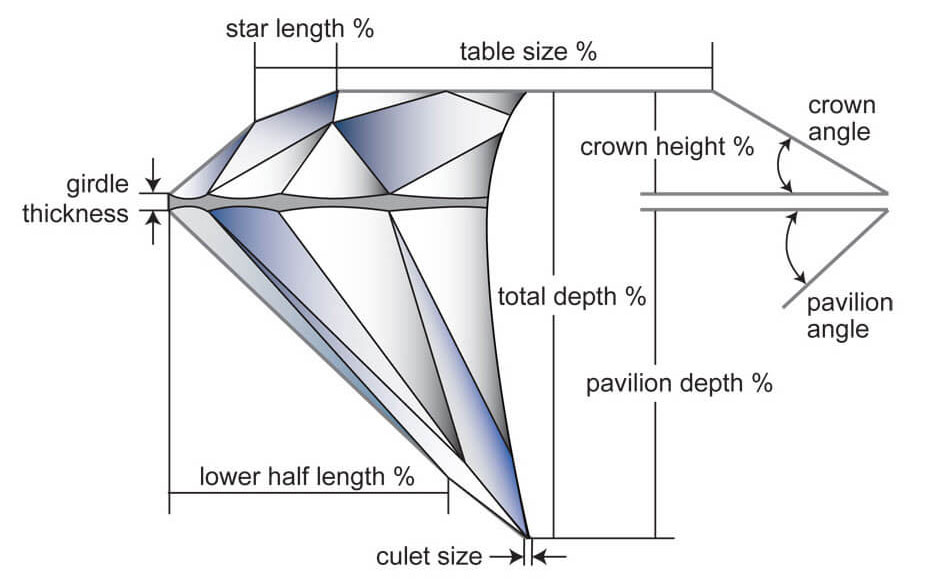
1. Cut
Diamond cut is the summary of a diamond’s proportions evaluated using the attributes of brilliance, fire, and sparkle. While high marks of color or clarity affect a diamond, it’s the cut that defines its proportions and ability to reflect light.
The Diamond cut scale is measured from Poor to Excellent. The Cut Grade of a diamond directly impacts its beauty; if a diamond is designed, cut, and finished properly, it will have a much more desirable appearance, even when compared to diamonds of higher color and clarity grades.
2. Color
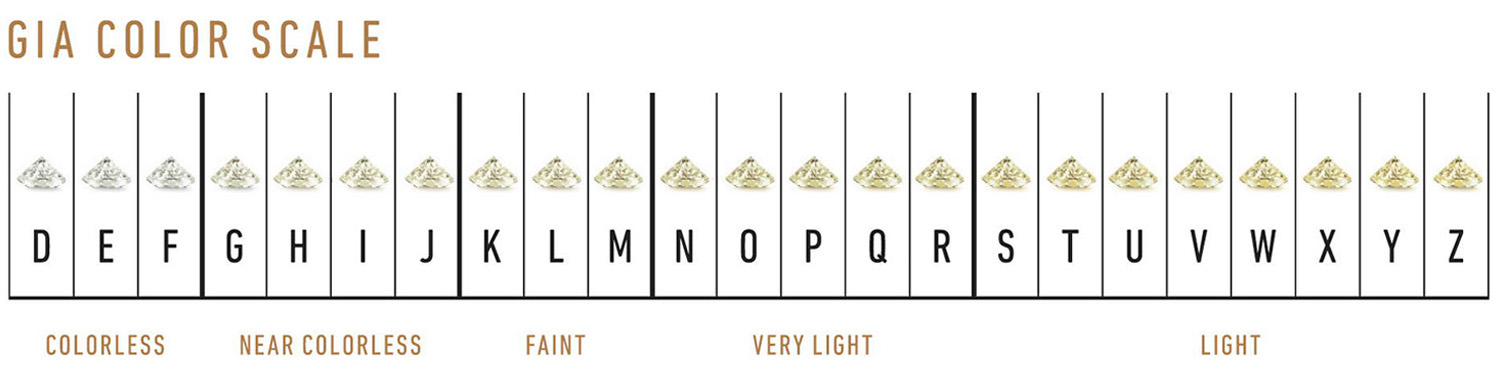

Tip
That’s why a “near-colorless” diamond is a safe bet if you plan to set it in yellow or rose gold jewelry, since the warm color of the metal makes any yellowness in the diamond less noticeable.
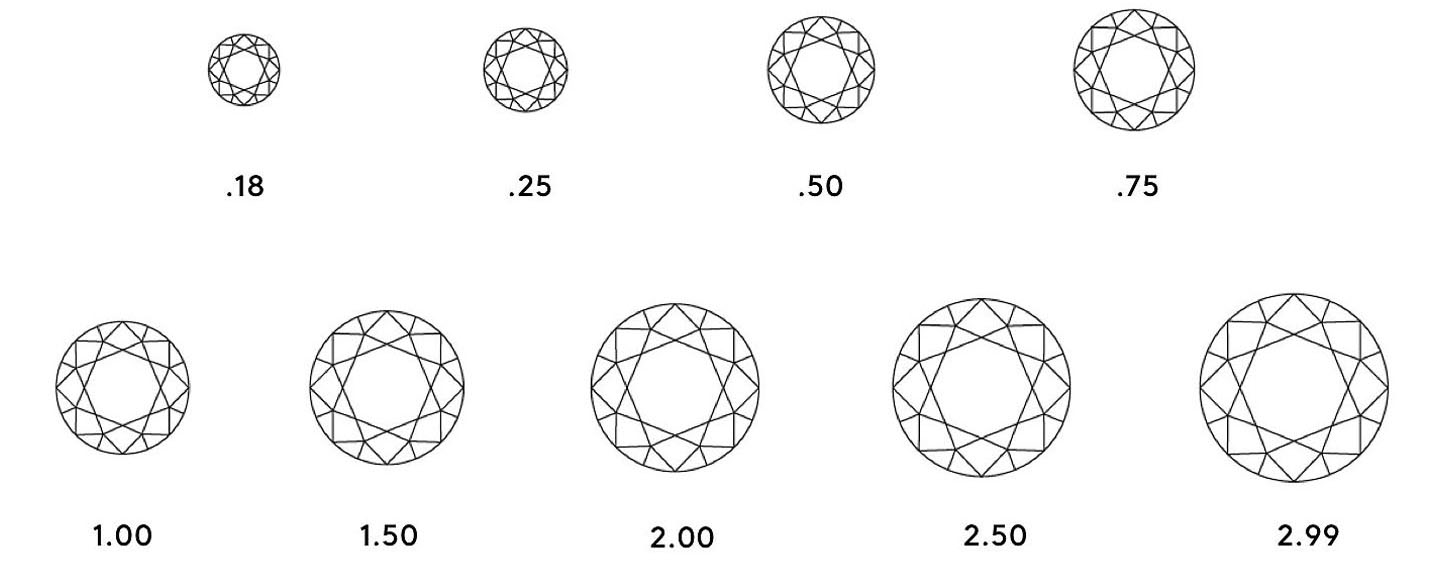
Choosing Your Carat Weight
When you’re ready to choose a carat weight for your diamond, remember that size is not everything – cut grade strongly affects the quality and beauty of your diamond; color and clarity grades do so too, though to a lesser degree.
For the best value, consider diamonds slightly lighter than the carat weight you initially had in mind. For example, if you are thinking about purchasing a 1.00 carat diamond, consider diamonds at 0.95 to 0.99 carats as well. The difference in visual size will be negligible, but the savings can be significant. You can use those savings to invest in a higher cut grade or a more lavish ring setting.
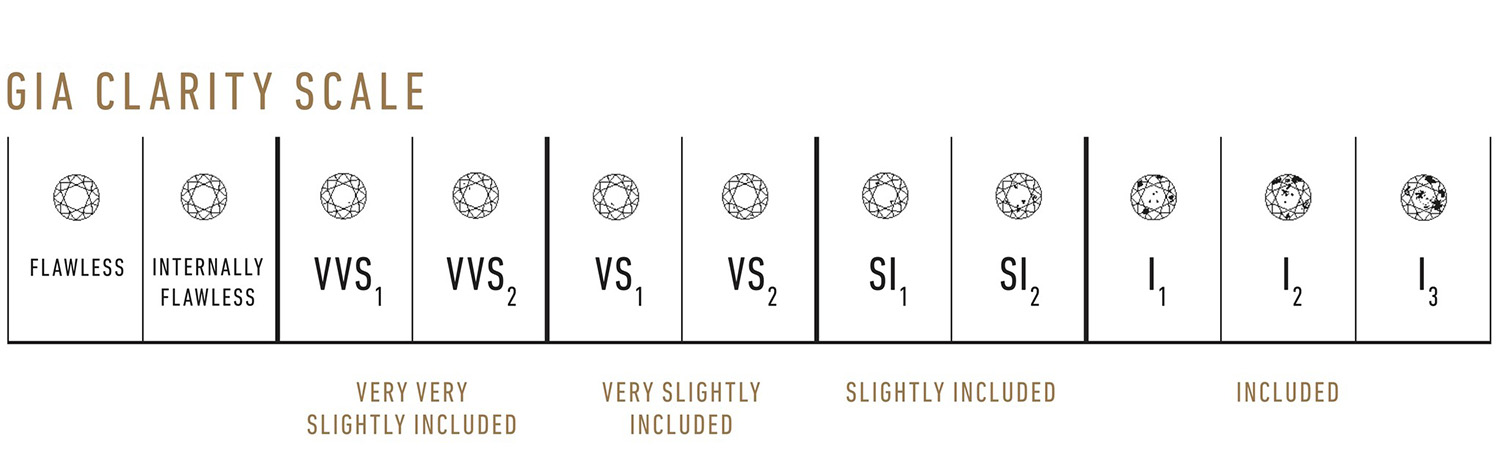
4. Clarity
Clarity refers to a diamond’s natural inclusions, or lack thereof. While small marks within a diamond are natural, their appearance can leave something to be desired if they are visible to the naked eye.
The shape of a diamond can affect the importance of its clarity grade. The facet patterns of the brilliant-cut diamond shapes, such as round and princess, can hide certain imperfections; while step-cut shapes, such as emerald and asscher, have large open tables that make inclusions more obvious.
The lowest clarity grade within The Diamond Store’s inventory is SI2. These diamonds may have small visible inclusions. If you are searching for a step-cut diamond, we suggest a minimum clarity grade of VS2.
If you want to rest assured that your diamond will display a clean and stunning brilliance, a clarity grade of VS1 or higher is recommended for all diamond shapes.

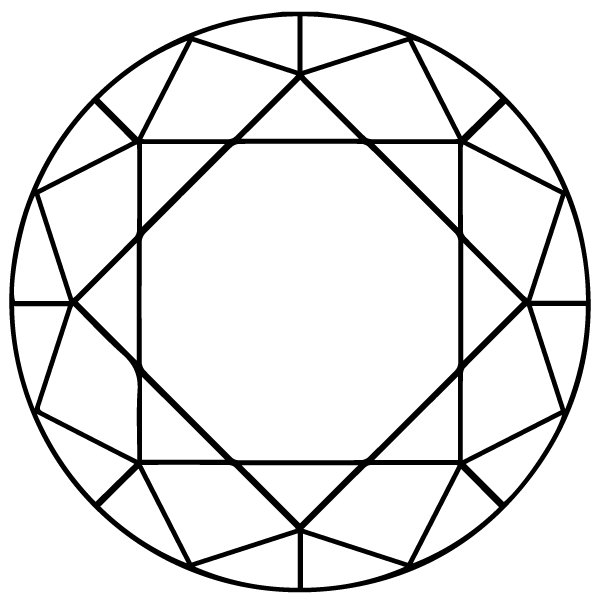
What is a diamond shape?
The Diamond shape refers to the geometric appearance of a diamond. Diamond shapes are categorized into two groups: round diamonds and fancy shape diamonds. Round diamonds, also known as round brilliant cuts, are the most traditional diamond and sparkle the most. Fancy shape diamonds refer to any diamond that is not a round brilliant. Our fancy shape diamonds include princess, cushion, radiant, emerald, pear, marquise, heart, and many more.